Fatigue Settings (Add to Company Settings)
There are two Custom Company Settings, and one company setting for determining which crew role combinations are considered multi crew.
Max Time Fatigue Rule Calculation Mode
This setting will determine how the maximum time for single and multi crew fatigue rules are calculated when there is a mix of single and multi crew time in a given duty period.
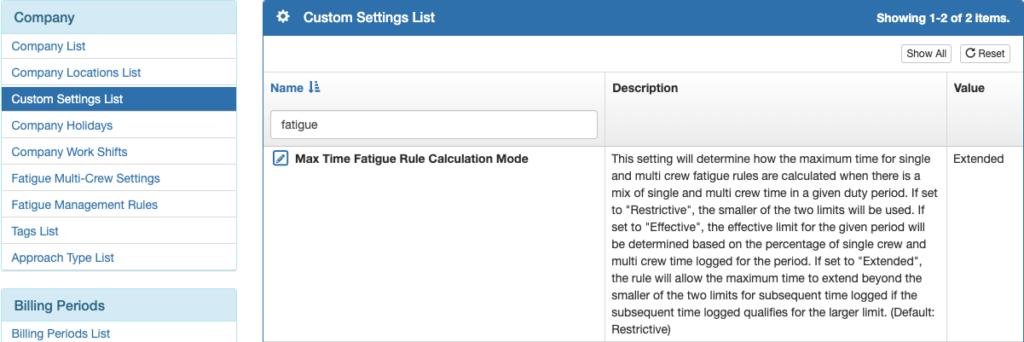
Restricted Mode: If the period being evaluated has a mix of single crew and multi crew flights within the time period, the lower of the two flight and duty time limits are used. Restricted Mode is the default setting.
For example, if the 24 hour limit for single crew flight time is 8 hours and multi crew is 10, and a pilot flew solo for 6 hours and then with an SIC for 3 hours, there would be a 1 hour exceedance on the second flight.
Extended Mode: If the period being evaluated has a mix of single crew and multi crew flights within the time period, a flight or duty period may exceed the lower of the two limits if it is of the higher limit crewing type.
For example, if the 24 hour limit for single crew flight time is 8 hours and multi crew is 10 hours, and a pilot flew solo for 6 hours, and then with an SIC for 3 hours, the pilot has 1 hour of available multi crew time remaining. But if the first 6 hour flight was multi crew and the second 3 hour flight was single crew, there would be a 1 hour exceedance.
Effectively this means that regardless of the time period being measured, if a pilot is flying a mix of both multi and single crew, once their total flight or duty time reaches the single crew limit, they will only be able to fly multi crew without causing an exceedance.
Effective Mode: If the period being evaluated has a mix of single crew and multi crew flights within the time period, the percentage of each crewing type is used to calculate the flight and duty time limits of the given period.
For example, if the 24 hour limit for a single crew flight time is 8 hours and multi crew is 10 hours, and a pilot flew solo for 4 hours and then with an SIC for 5 hours, there would be no exceedance. The first 4 hour flight is 50% of the 8 hour single crew limit, and the second 5 hour flight is 50% of the 10 hour multi crew limit. This means the pilot has an effective limit of 9 hours, and they have used 100% of their effective limit.
As the current time changes, the percentage of crewing changes as flight or duty time is added or removed from the evaluation window, so the effective limit also changes. This change in effective limit can cause the effective limit to increase or decrease faster than the total flight or duty time. For this reason, the moment of maximum exceedance is calculated.
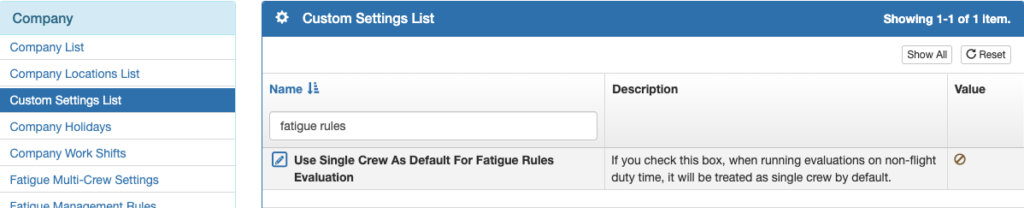
Fatigue Rules For Non-Flight Duty Time
If this setting is checked, pilot duty time without any flight records will be processed according to the single crew duty time and rest rules. If not checked, the multi crew duty time and rest rules will be used.
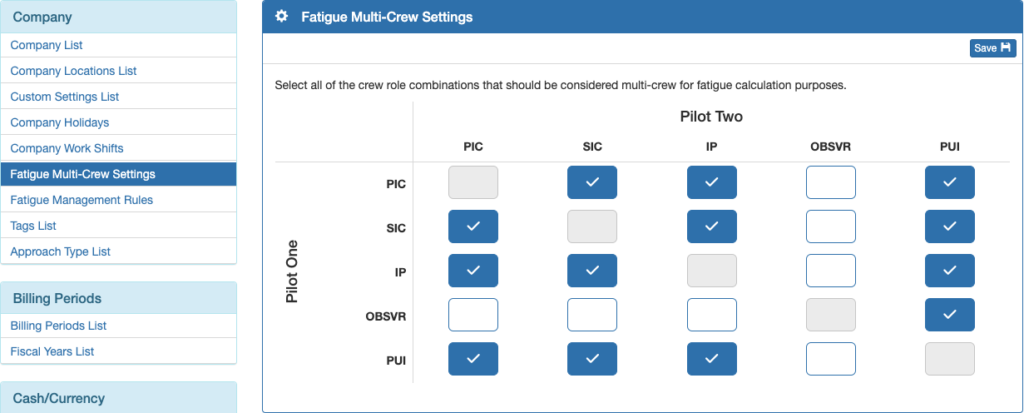
Fatigue Multi-Crew Settings
Set which combinations of pilot roles are considered multi-crew from Fatigue Multi-Crew Settings on the Company menu. In the example below, all combinations are considered multi crew except if a pilot is assigned the Observer role.
If no combinations have been set, all flights will be treated as single crew, regardless of how many pilots are on board.
Note: If no crew role has been assigned for the second pilot, FlightSpan™ will not record the second pilot on the flight.
Fatigue Rules
Select Fatigue Management Rules from the Company menu, and edit the values directly in the window that opens.
You can set maximum Flight Time limits, maximum Duty Time limits, and Rest Requirements for single crew, multi crew, and maintenance.
Be sure to save your work before exiting the page.
Recording Duty Time (Document 1)
Missing data (Document 2)
Because FlightSpan™ cannot accurately calculate flight and duty time without accurate flight or duty time records, there are flags in several places alerting you to missing data.
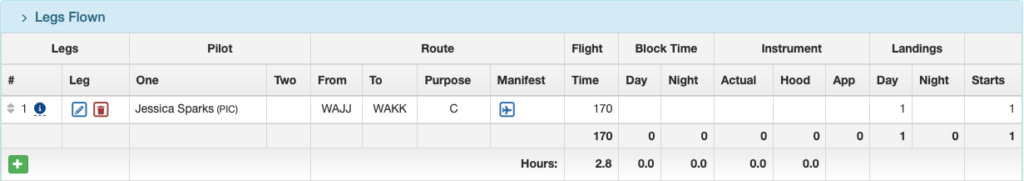
On the Flight Records List page, the pilot is flagged if the record is missing duty time; the flight time is flagged if it’s missing ATD/ATA.
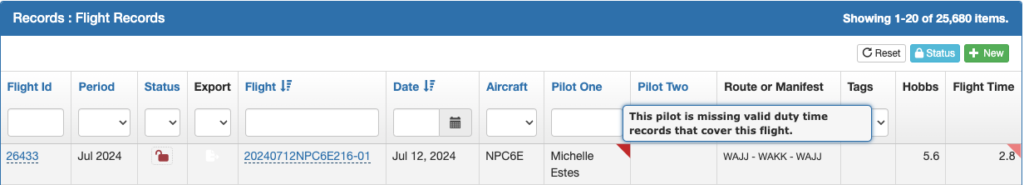
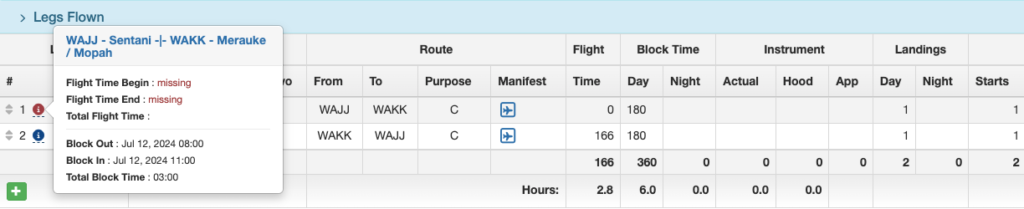
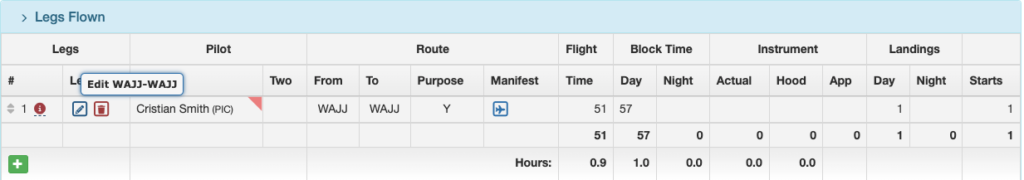
The Legs Flown section of the Flight Record Detail will also be flagged.
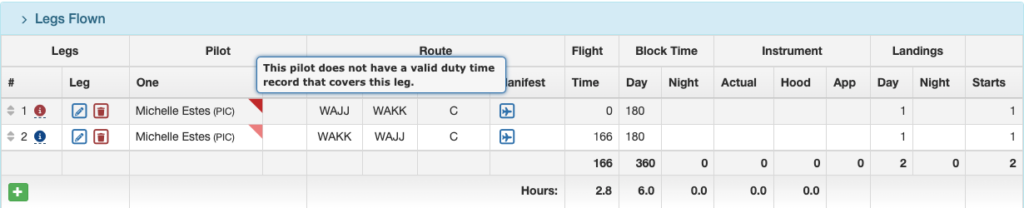
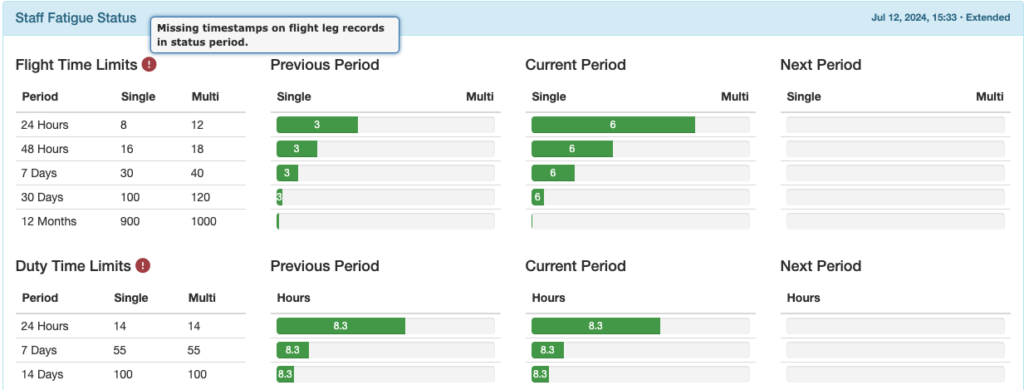
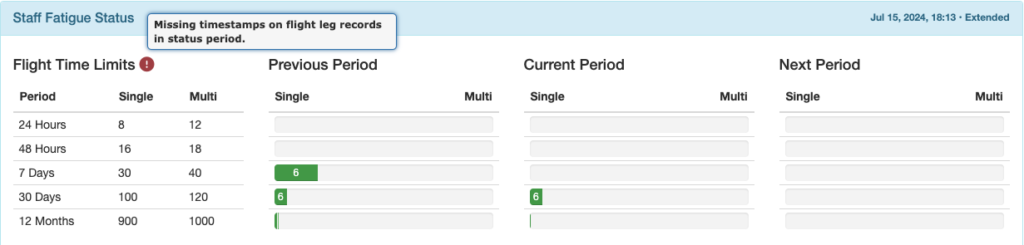
The Staff Fatigue Status Flight Time Limits and Duty Time Limits sections will also be flagged.
Resolving Missing Flight Times
If flights are uploaded without an ATD or ATA, flight legs missing the ATD or ATA will not be displayed on the Flight Time Limits graph.
Select the blue pencil icon to open the flight leg.
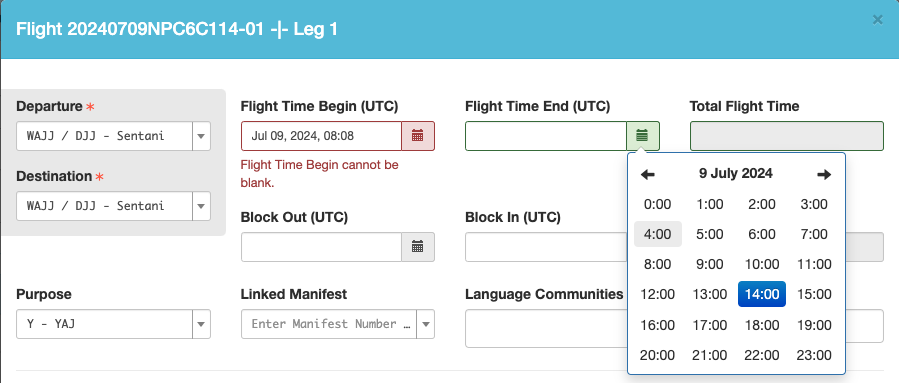
Add the missing beginning and ending times, as well as Block Out and Block In as necessary, and save.
Once there are valid ATD / ATA times the flight will be displayed and the badge will be removed.
Flights that are uploaded without Block times will default to flight time for the Flight Time Limits calculation (or to flight time plus one tenth depending on the Company Custom Setting for logging pilot flight time).
Resolving Missing Duty Times
Flights that are uploaded without duty time will be flagged, but FlightSpan™ will use your company’s standard pre and post flight duty time intervals (applied prior to the first leg and after the last leg) to generate the Duty Time Limits and Rest Timeline graphs. (No duty time record will be created.)
From the Flight Record
There will be a red banner at the top of the flight record to resolve missing duty time.
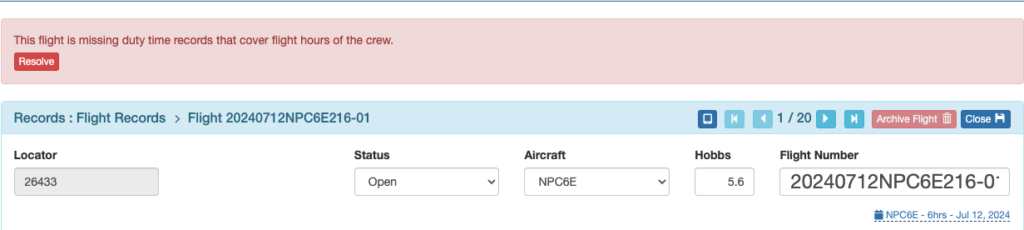
If you click the Resolve button, it will jump to the bottom of the record where you can click the green Add Duty Time button.

If there are valid ATD/ATA records, the duty time will be prefilled with the default duty time before and after the flight.
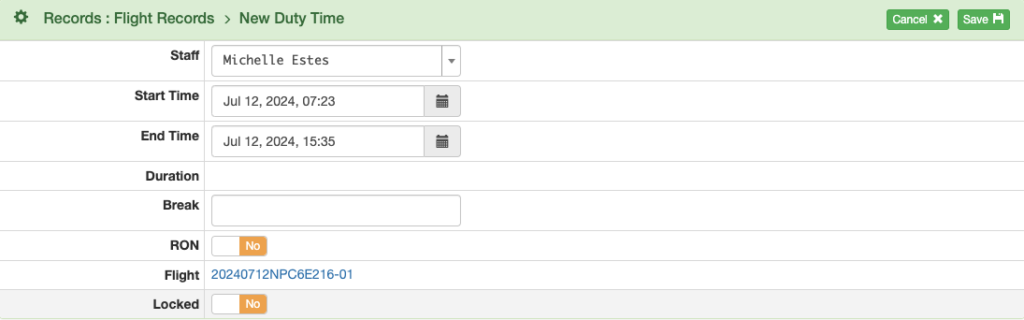
Select RON Yes if the pilot remained overnight; select Lock Yes to lock the record and prevent further editing.
If there are overlapping duty time records, you will not be able to save the record.
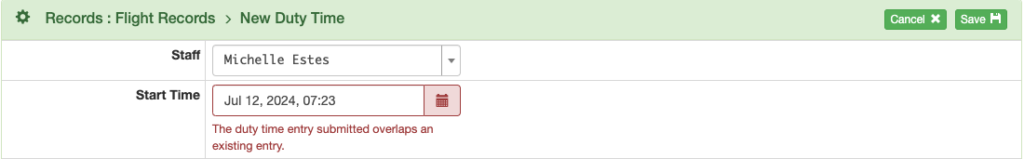
If necessary, open the Pilot Detail to correct the duty time entries by clicking on the blue pencil icon, or delete duplicate entries with the red trash can icon.
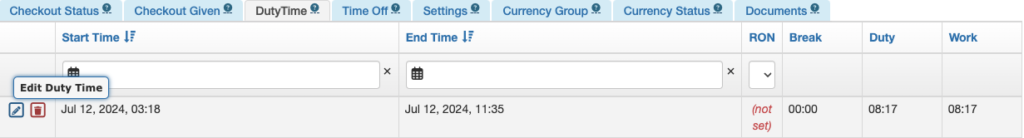
From the Pilot Detail
From the Duty Time tab of the Pilot Detail, scroll down to the bottom and click the green plus button to add a new duty time entry, or the blue pencil icon to correct a duty record.
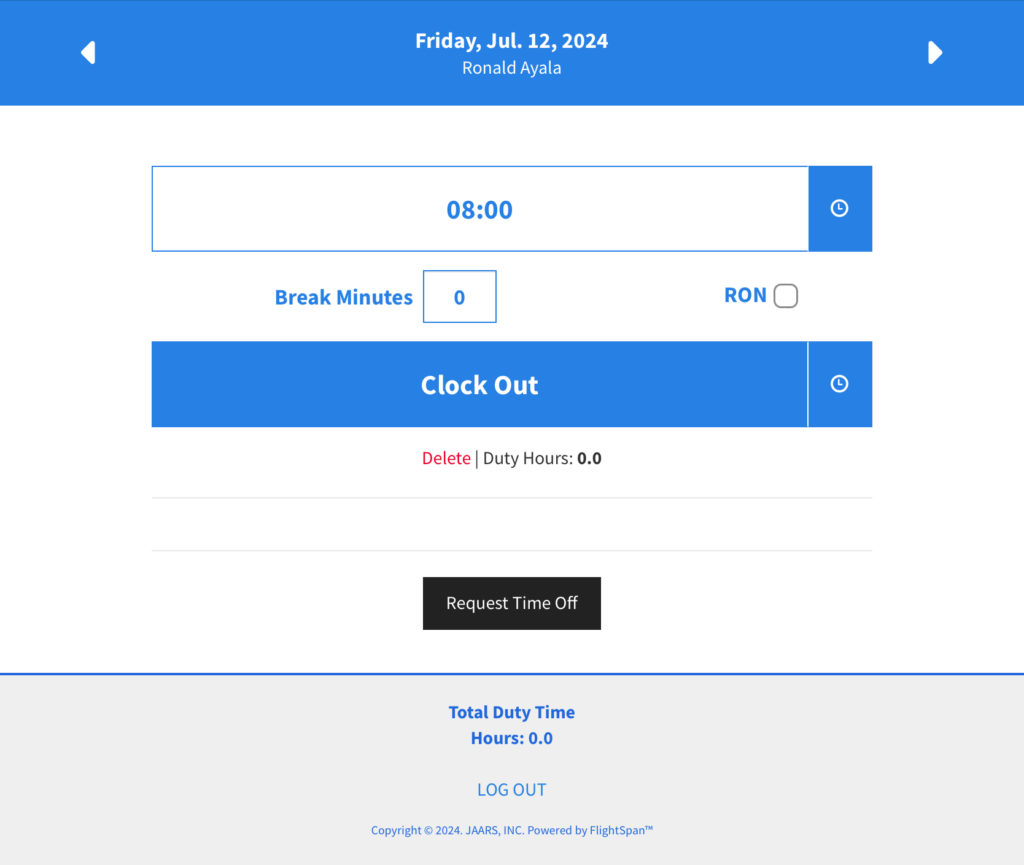
From Your Personal Device
Open the duty time page on your personal device, and create a duty time entry.
Closing Open Duty Periods
There will also be a flag if a duty period was not closed.
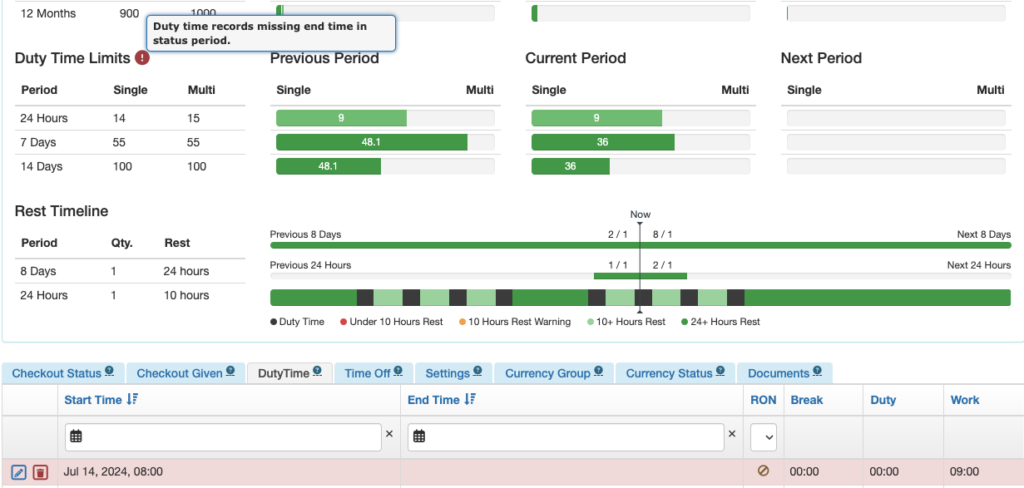
There are several ways to close an open duty period.
The pilot can select My Settings from the Settings Menu, and open the Duty Time tab.
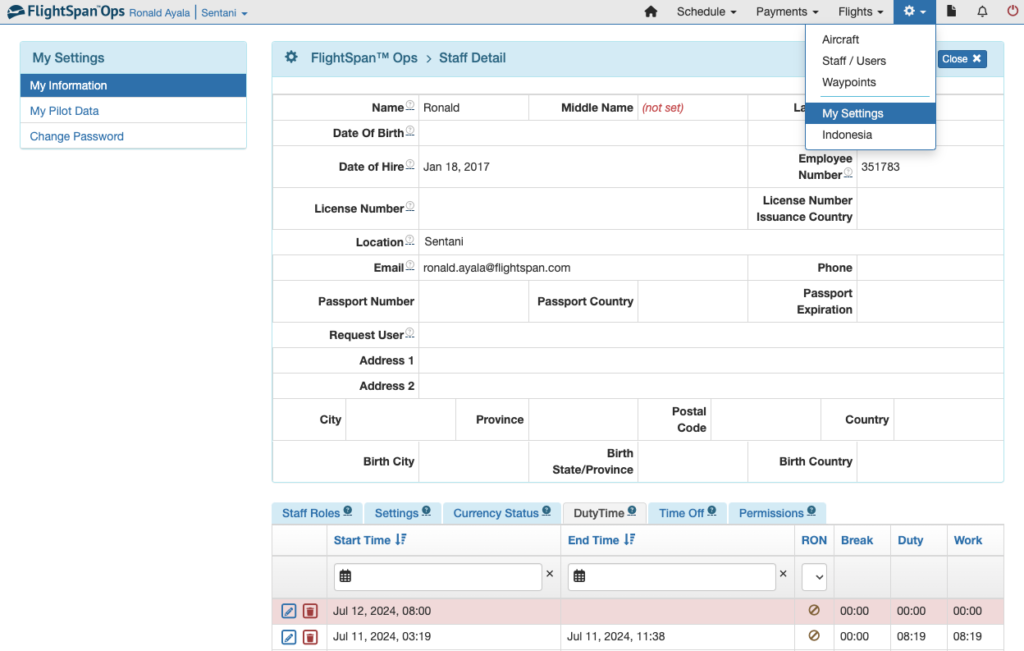
Or select My Pilot Data from the My Settings menu on the left, which will open the Pilot Detail with the Duty Time tab already open.
From both locations use the blue pencil icon to edit the open duty record.
Another way is for the supervisor to go to the Duty Time List where individual duty records are listed.
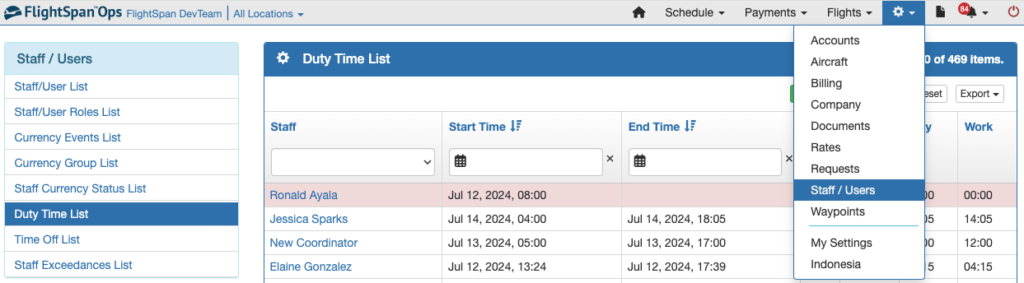
Click on the pilot’s name next to the record to see the record details, and delete or edit as desired.
Finally, a pilot can use the duty time page on their personal device, navigate to that date, and clock out.

Exceedance Records (Document 3)
From the Staff / Users menu select Staff Exceedances List. Click on the staff member name to open an exceedance record.
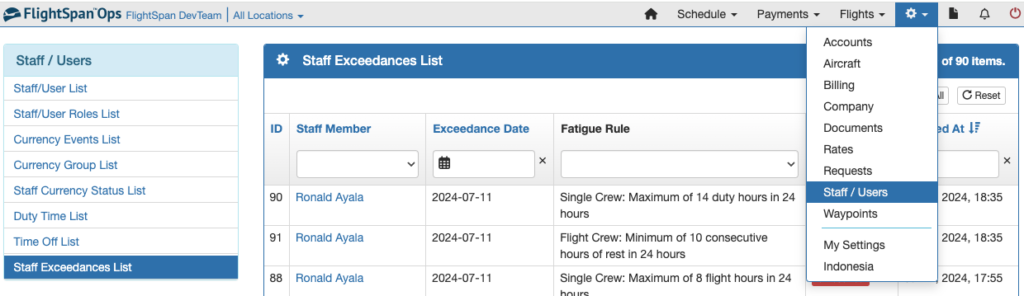
Exceedance records are permanent, and cannot be deleted; however their status can be changed. There are three statuses.
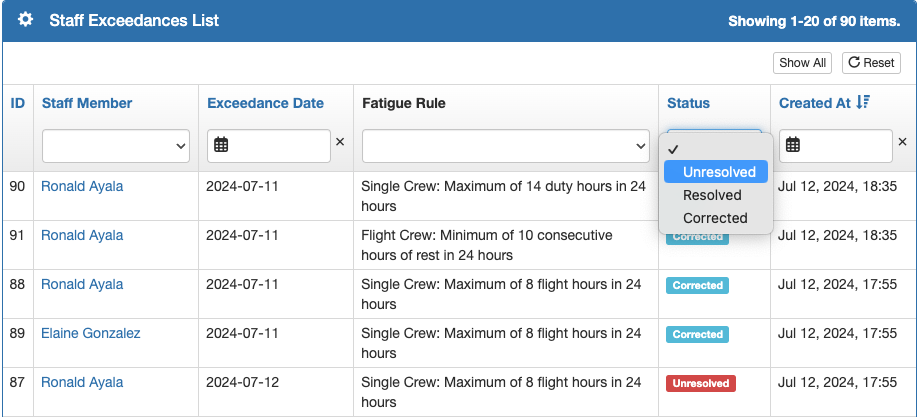
Unresolved – no action has been taken.
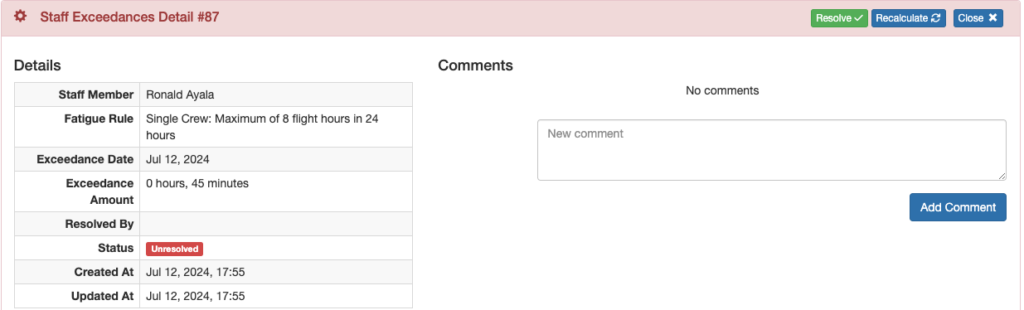
Resolved – the chief pilot or their designee took action to mitigate the effects of the exceedance.
Select the green Resolve button, and add a required comment to explain how the exceedance was resolved.
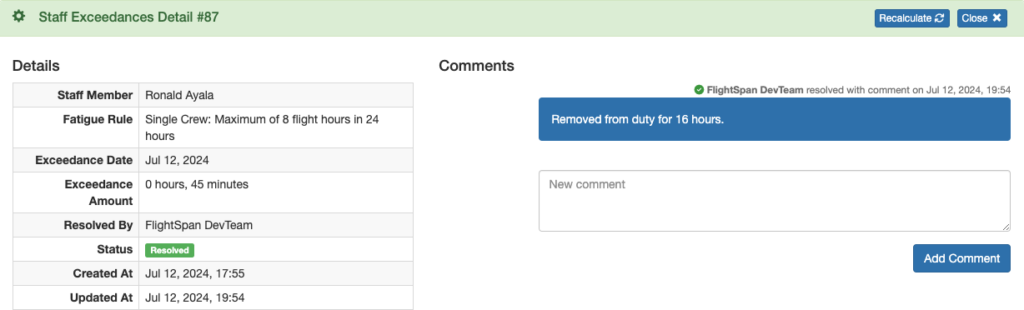
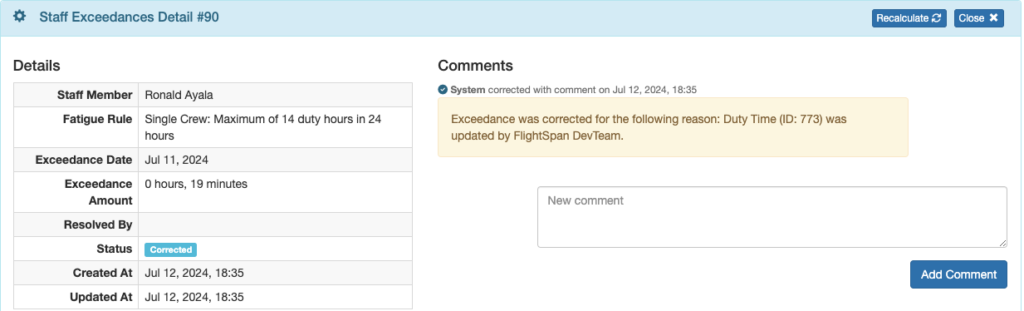
Corrected – a record was corrected to eliminate the exceedance. A system generated comment records the change that was made.
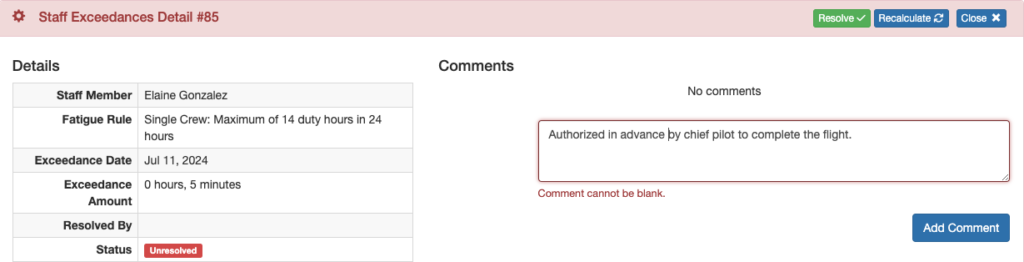
A comment can be made on any record with the blue Add Comment button.
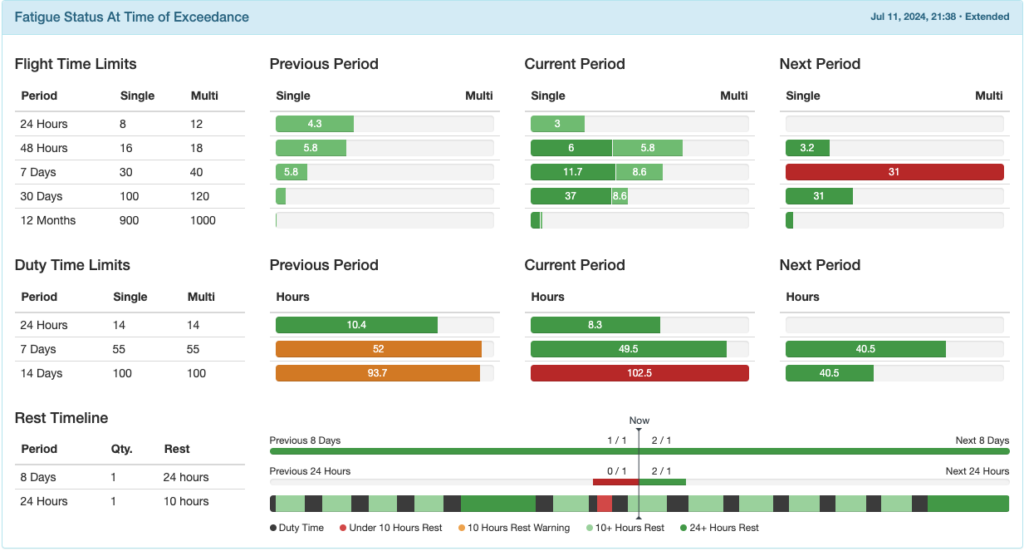
At the bottom of the exceedance record, the fatigue status at the time of the exceedance is recorded.
Any time an exceedance is generated, there will be a notification in the header bar. Click on the notification to open the exceedance record.

Note: All exceedances are calculated at the leg/segment level. This means that a record may have multiple exceedances if both the single and multi crew limits were exceeded.
Staff Fatigue Status (Document 4)
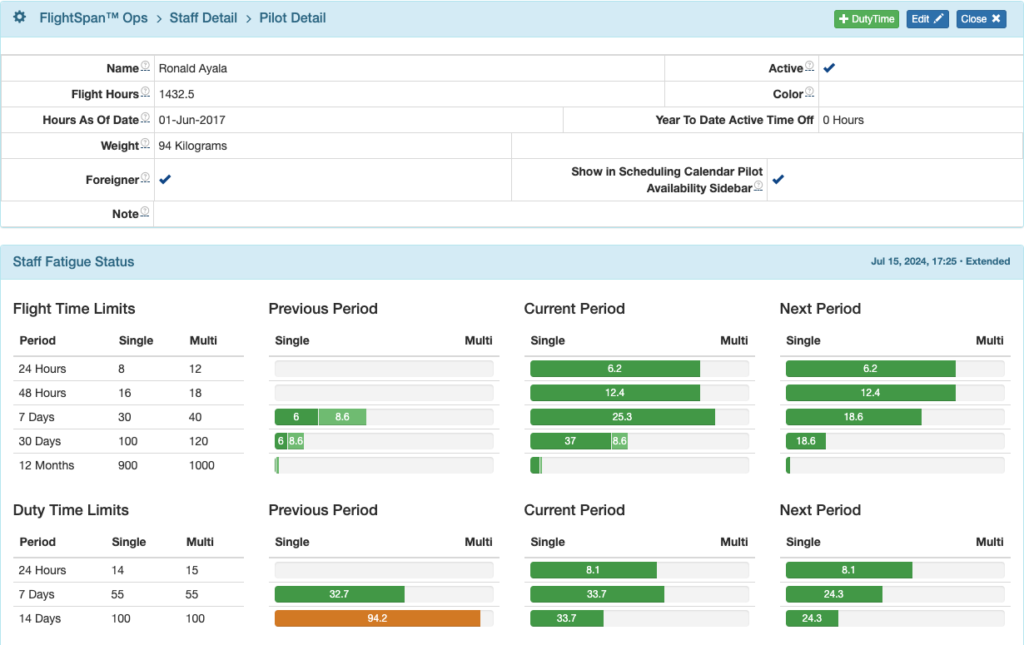
Staff fatigue status is displayed on the Pilot Detail page.
Self Monitoring
Pilots can monitor their own duty and flight time from their My Pilot Data page.
If you have added the shortcut to the Home page click on the Pilot Data icon, or from any page, select My Settings from the Settings menu at the top.

Then select My Pilot Data on the left.
The Pilot Detail will open, with the Staff Fatigue Status records.
Chief Pilot Monitoring
The chief pilot or his designee can monitor all of the pilots from the Pilot Detail page.
Select Staff / Users from the Settings Menu.
Then click Pilots List on the left, and click on the first pilot’s name.
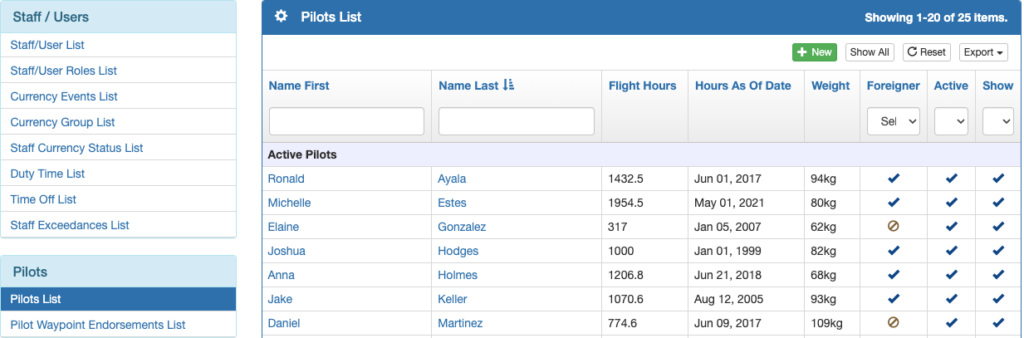
Review the record, then use the arrows to scroll through the list of pilots, checking each one as you go.
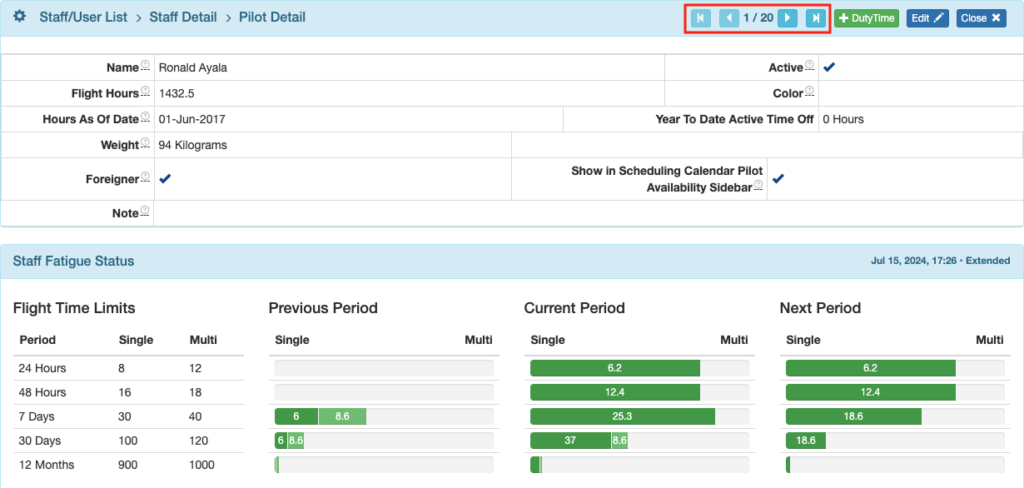
Interpreting the Data
Color coding is as follows:
- Green = Less than 90% of the limit
- Yellow = 90-100% of the limit
- Red = limit exceeded
Under Flight Time Limits there is additional color coding:
- Solid color = single crew flight time
- Light color = multi crew flight time
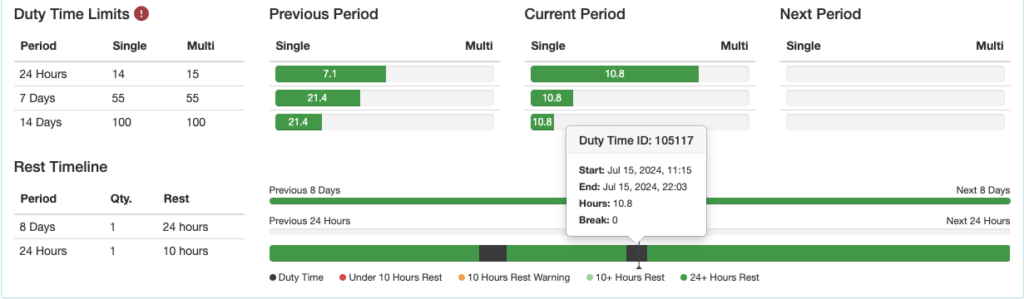
The current date and time is displayed in the upper right corner along with the fatigue calculation mode.
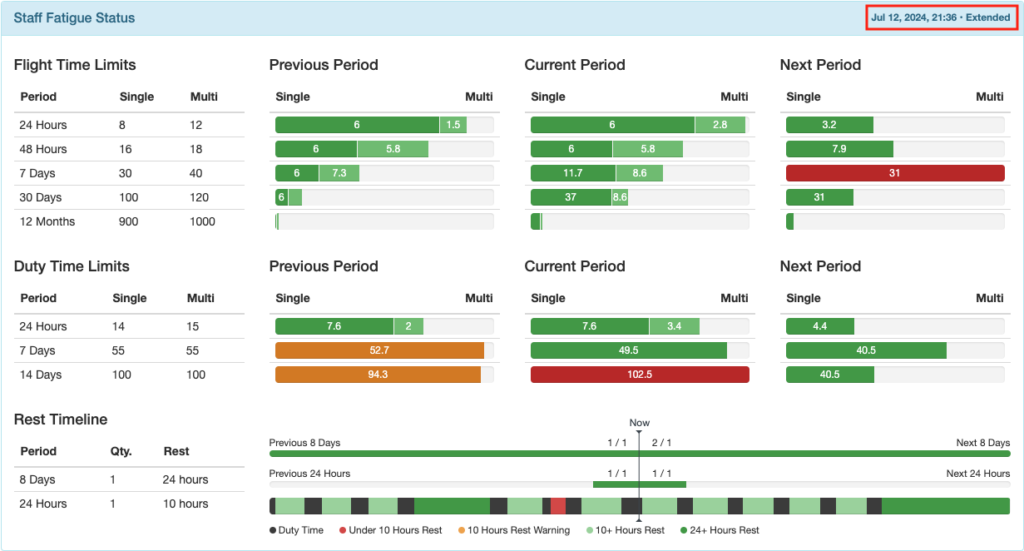
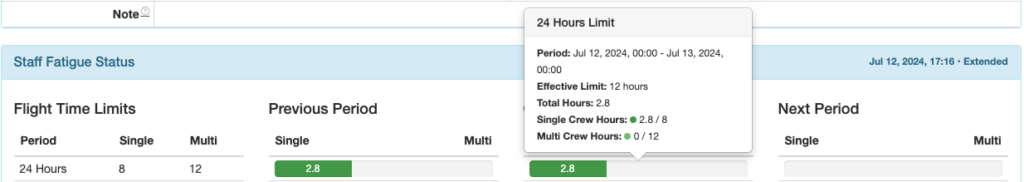
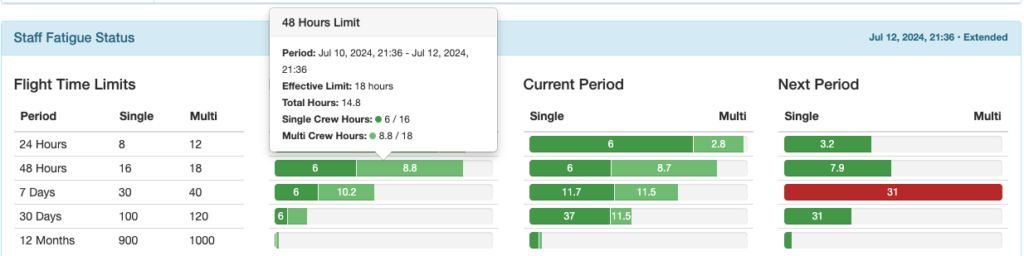
Previous Period Column: Begins right now and looks back the specified amount of time.
In this example, the pilot flew 6 hours single crew and 8.8 hours multi crew in the 48 hours between July 10 at 21:36 and now (July 12 at 21:36).
Hover over any status bar for details.
Current Period Column: A fixed period that varies based on the window being measured. For example, 24 hours is midnight last night to midnight tonight; 7 days, 14 days, and any other multiple of 7 days is midnight Sunday to midnight Sunday.
Any arbitrary length period such as 48 hours starts at midnight the first of the year, so the first period would be midnight January 1 to midnight January 3; the second period would be midnight January 3 to midnight January 5, and so on. Months are 30.4 day periods (365.25 / 12) starting at midnight on January 1.
In this example, the pilot exceeded the 14 day duty time limit during the current period of midnight June 30 to midnight July 14.
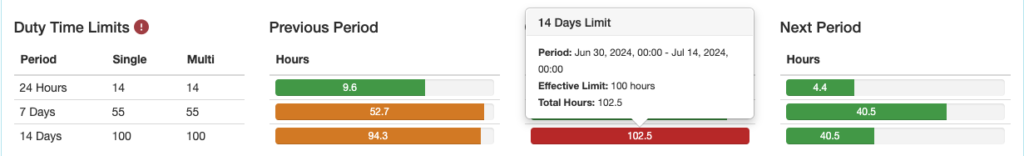
Next Period Column: Begins right now and looks ahead the specified amount of time.
In this example, the pilot is scheduled to fly for more than the 30 hour single pilot limit between now (July 12 at 21:36) and July 19 at 21:36.
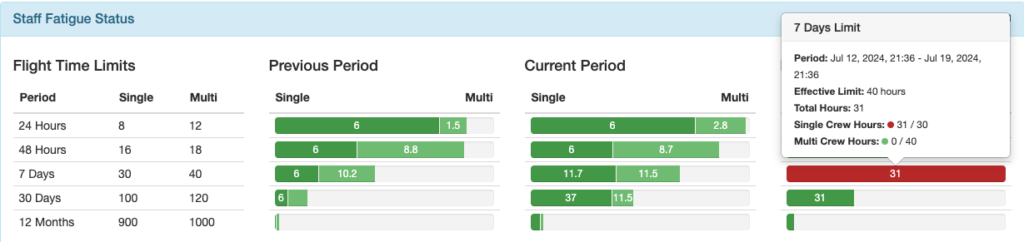
Note: Flight time is calculated based on ATD and ATA, which is recorded in minutes, and duty time is calculated based on the recorded starting and ending times of the duty period. Displayed flight and duty time are both rounded to the nearest tenth of an hour, so it is possible to appear to be within the limit when an exceedance is generated. For example, the daily duty time limit is 14 hours, and the duty time record shows 14.0 hours, but since the pilot worked 14 hours and 2 minutes, an exceedance is generated.
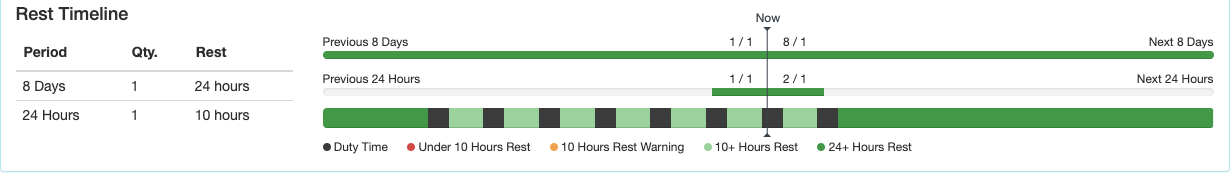
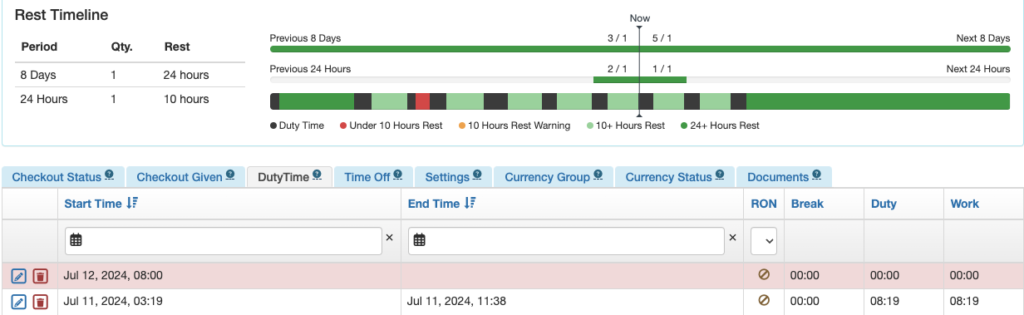
Rest Timeline
The bottom row indicates periods of duty and rest. It is color coded according to the key below the row. Hovering over each segment gives the details.
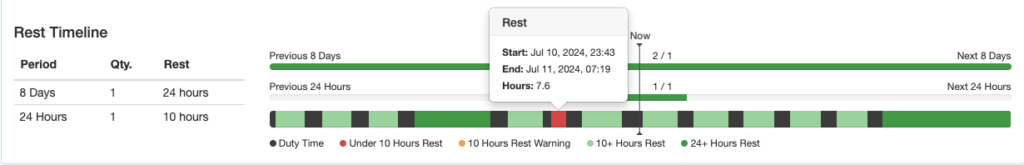
The first row indicates how many of the required rest periods the pilot has had, or is scheduled to have. In this example, the pilot has had 1 of 1 required 24 hour rest periods in the previous 8 days, and is scheduled for 2 of 1 required rest periods in the next 8 days.
The second row also indicates how many of the required rest periods the pilot has had. In the last 24 hours, the pilot has had 1 of 1 required 10 hour rest periods.
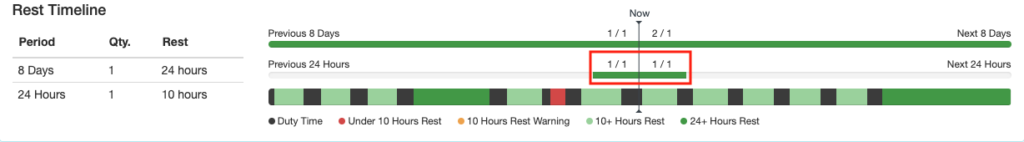
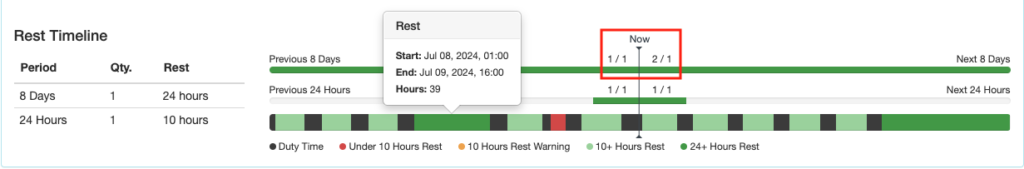
If any past work or future scheduled flights violate the rest rules, the bars will turn red.
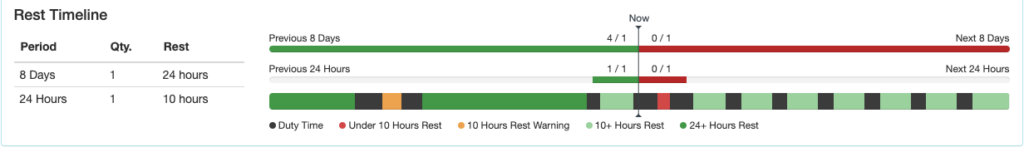
The 24 hour row will turn red if there are not 10 hours of consecutive rest in the 24 hour windows, so depending on when you look at the record, it may be red even when rest times are being properly observed. An exceedance will not be generated.
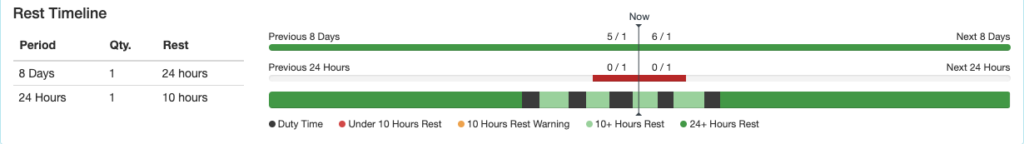
Note that until the future rostering feature is developed, the system will not warn if past work plus future scheduled exceeds the rest requirements. In this example the pilot’s past work plus future scheduled exceeds the 24 hours rest in 8 days rule, but no warning is generated.